

These differences in isotopic abundance are used as “labels” to identify the different sources of CO 2 found in an atmospheric CO 2 sample. If you have any queries regarding Atoms and Molecules CBSE Class 9.
C 12 ATOM PDF
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules with Answers Pdf free download will help you. Use the data given in table mentioned below. Certain isotopes are more abundant in some materials than others since some physical and chemical processes “prefer” one isotope over another. Complete the following crossword puzzle by using the name of the chemical elements. Step 2: Mass of one atom of carbon - 12: Mass of one mole of carbon - 12 12 g. Step 1: Molar mass of carbon ( C): Molar mass of carbon 12 g mol - 1. The elementary entities may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an electron, or any other particle. Although isotopes of the same element are twins when it comes to reactivity, the different number of neutrons means that they have a different mass. This number is called Avogadros constant. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. Neutrons are neutral - they have no charge. For example, a carbon atom has six protons, but an atom with only five protons is boron while an atom with seven protons is the element nitrogen.
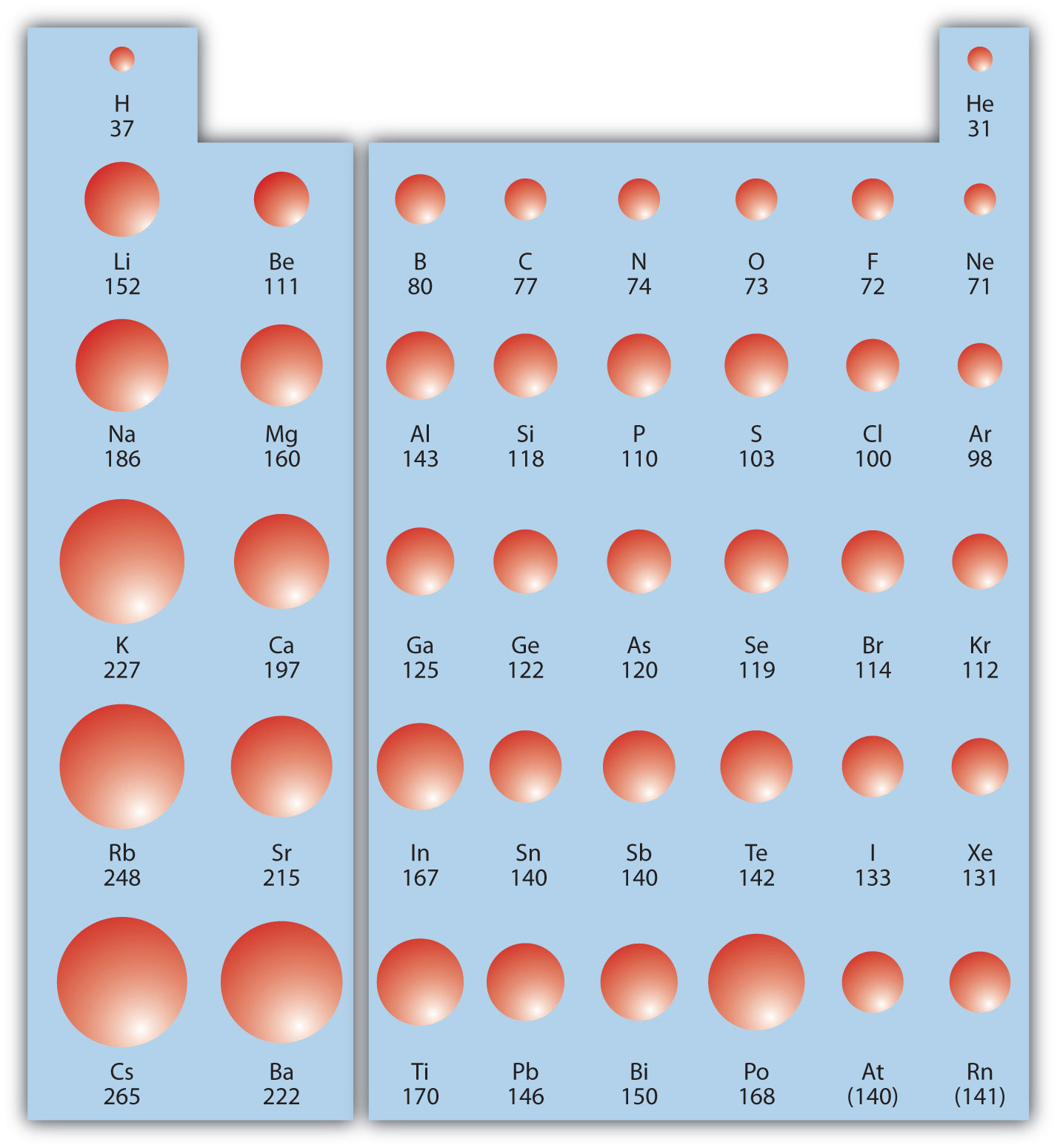
In other words, the number of protons is what gives each element its unique, individual identity. Protons are positively charged particles, and the number of protons is always fixed for a particular element. So, if we use '1/12th the mass of a C-12 atom' to define a unit of mass (let's call it 1amu), then the masses of other atoms are convenient integers like 3amu, 10amu, 50amu etc. If reference is changed to (1)/(24) th of mass of single atom of C-12 new scale, then select the correct statement(s). The small, dense nucleus (or center) of the atom contains the other components–the protons and neutrons. As it turns out, most atoms have masses that are approximately convenient integer multiples of 1/12th the mass of a C-12 atom. Atomic mass of elements are defined with respect to (1)/(12) th of mass of single atom of C-12 present scale. It then passes them through a velocity selector consisting of uniform E and B fields that keep the ions traveling in a straight line. However, the atom remains the same element whether it has a positive, negative, or neutral charge. Transcribed image text: X Mass Spectrometer Example A mass spectrometer takes singly ionized atoms (q +1.6 x 10-19 C) and accelerates them through a potential difference. Atoms may gain or lose electrons, which change the charge of the atom (creating ions). Although atoms are too small to see without using high-powered microscopes, they are composed of even smaller particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.Įlectrons, which are extremely light, negatively-charged particles, orbit around a central mass–the nucleus of an atom. The Technical Details: Chemistry Composition of an AtomĪtoms, which are the basic, fundamental unit of all matter, can differ greatly from one another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
